Not only get subsidies, but also save taxes!
investment credit
There are many benefits of innovative research and development
Subsidies and tax savings
kill two birds with one stone
Innovative research and development can not only get subsidies, but also save taxes!


Light Tax and Simplified Administration Policy
In line with the tax system reform direction of "light taxation and simplified administration", the income tax rate for profit-seeking enterprises has been reduced from 25% to 17% (the reduction rate has reached 32%), and tax incentives must control a certain amount of tax expenditure (10 billion yuan), according to the Industrial Innovation Regulations Only the research and development investment deduction function-specific tax incentives are retained.


Encourage industrial innovation with offsets
In order to encourage companies to continue to engage in research and development to promote industrial innovation, the Ministry of Finance and Economics, in accordance with Article 10, Item 2 of the Industrial Innovation Regulations, jointly issued the "Investment Offset Measures Applicable to Company Research and Development Expenditures" on November 8, 1999. , a total of 17 articles.
| Strip number | tax incentives | Suitable |
|---|---|---|
| Article 35 | R & D investment | Small and medium enterprises for company registration |
| Article 35-1 | Intellectual property rights shareholding postponement | 1. Small and medium-sized enterprises that have gone through company or business registration according to law |
| 2 people | ||
| Article 36-2, Paragraph 1 | Tax deduction for hiring more than 2 employees of this nationality | Small and medium enterprises that apply for company or business registration |
| Article 36-2, Paragraph 2 | Increase the tax credit for employees under the age of 24 | |
| Article 36-2, Paragraph 3 | Grass-roots employees pay tax deduction |


Industrial Innovation Regulations
Production Innovation Article 10 Research and Development Investment Credit
(1) In order to promote industrial innovation, the company may invest in research and developmentfifteen percentwithin the limitcurrent yearThe amount of income tax payable for profit-seeking enterprises.
(2) and not exceeding the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable by the company in the current yearthirty percentlimit.
(3) The offset method is determined byThe central competent authority and the Ministry of FinanceSet it.



labor promotion regulations
Production Promotion Article 6 Research and Development Investment Credit
(1) The company may spend on research and development and personnel trainingthirty five percentwithin the limit, sinceWithin five years from the current yearOffset the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable in each year.
(2) The company's research and development expenditure in the current year exceeds the average amount of research and development expenditure in the previous two years, and the excess part shall be paid according to thefifty percentOffset it.
(3) For the investment deduction in the preceding two items, the total amount of the deduction in each year shall not exceed the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable by the company in the current yearfifty percentlimit. However, the deduction amount in the last year is not subject to this limitation.
(4) The offset method is determined byExecutive YuanSet it.
Applicable to research and development expenditure
Investable Offset Items
Engage in innovative research and development activities
Limited to "innovative" development, any activities to improve old products are not included
Research and Development Unit
Recognition criteria: determined by the central authorities in charge of the target industry according to the needs of industrial development and administrative operations
non-research and development unit
Allocate full-time R&D personnel to engage in R&D activities
Attached documents: personnel work content, time records, activity records, etc.
Recognized by the central target business authority
deductible expenses
Salary, database software programs, patent works, samples, raw materials, etc.
recognized by the IRS
Industrial Innovation Regulations
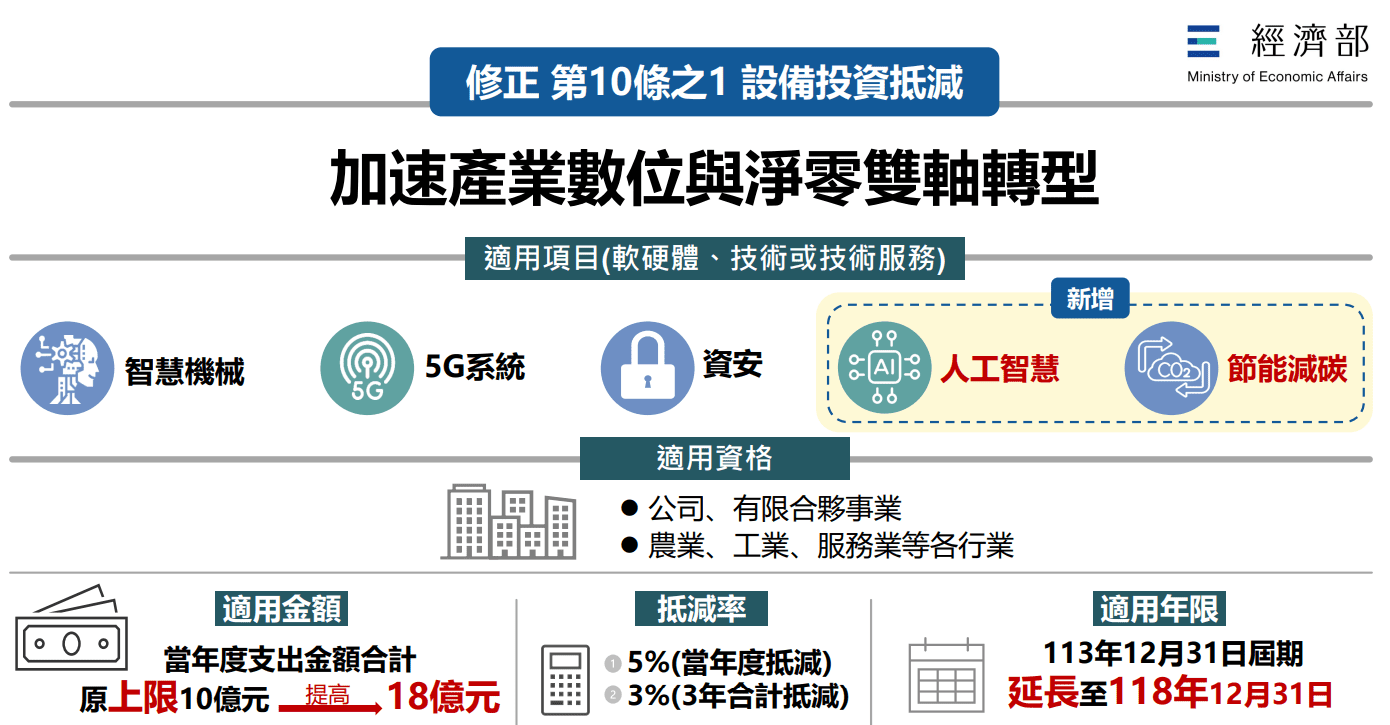
智慧機械、5G、資安、人工智慧及節能減碳 投資
皆可享投資抵減
Innovative research and development can not only get subsidies, but also save taxes~
為協助產業數位化及低碳化雙軸轉型,協助新創事業募資,強化公司對外投資的同時保護關鍵技術,行政院會19日拍板「產業創新條例」部分條文修正草案,延長投資抵減優惠至2029年底,新增人工智慧(AI)及節能減碳兩項目,並將申請適用金額上限由10億元提高至18億元。經濟部說明,相關租稅優惠條文自2025年起適用。
經濟部表示,因應「產創條例」第10條之1將於2024年底屆期,以及AI創新應用及節能減碳趨勢,本條文保留智慧機械、5G及資安項目,並另納入AI及節能減碳,有助於引導台灣百工百業投資相關設備,落實AI化與低碳化雙軸轉型;另為配合產業投入智慧化、AI及低碳化等相關設備,申請適用金額上限由10億元提高至18億元,延長優惠至2029年12月31日止,可更為貼合產業升級轉型所需。經濟部指出,為協助新創事業發展,本次亦同步修正第23條之1與第23條之2,其中第23條之1部分,將有限合夥創投事業的實收出資額門檻從現行3億元降為1億5,000萬元,並提高第3年度起投資新創事業須達一定金額或比率,以鼓勵創投事業及早投入更多資金於新創事業。
經濟部補充,天使投資人投資新創亦有租稅優惠,第23條之2投資門檻從現行100萬元調降為50萬元,而投資對象為5年內的新創事業,皆可持續獲得資金協助,且天使投資人投入的產業範圍屬國家重點發展產業者,每年可減除金額上限提高到500萬元,以協助新創事業取得資金。
經濟部表示,為保護關鍵技術及維持產業競爭力,第22條修正草案,透過聚焦投資管理範圍,除投資達一定金額應事前申請核准外,另增列投資於特定國家或地區、特定產業或技術等情形亦須事前申請;同時增訂第67條之3中央主管機關配套管理權限,未申請核准實行投資,處新臺幣5萬元以上100萬元以下罰鍰,而未改正、停止或撤回投資,處50萬元以上1,000萬元以下罰鍰。
經濟部說明,本次修正施行後,期可帶動產業升級轉型、推動新創事業發展,更能保護關鍵技術。期望本次修正案送請立法院審議能儘速通過,俾利法案順利實施,形成台灣產業轉型升級的助力。
資料來源:工商時報/經濟部工業局 智慧機械及5G系統投資抵減官網

Global Trademark and Copyright Application
Smart Machine Definition


smart technology elements
(1) Sensor:
Refers to a device used to detect events or changes in the environment and transmit information to other electronic devices.
(2) Internet of Things:
Refers to information carriers such as the Internet and traditional telecommunication networks, which enable all ordinary objects that can perform independent functions to realize interconnection and intercommunication.
(3) Mass data:
Refers to huge-scale data, which can be used to make decision-making suggestions and create innovative value through data collection, data storage, information extraction, and statistical analysis.
(4) Integration of reality and reality:
It refers to the communication and interaction between physical and digital systems through the use of virtual, simulated or networked software technologies such as mechanical equipment and manufacturing procedures.
(5) Artificial intelligence:
Refers to the computer system having human knowledge and behavior, and having the ability to learn, reason and judge to solve problems, memorize knowledge or understand human natural language.
(6) Lean management:
It refers to eliminating waste through management methods and improving manufacturing and service processes to increase production efficiency and reduce production costs.
(7) (8) (9) Digital management:
Refers to process management, equipment management, production management, supply chain management, and customer relationship management that include digital software technology. (Including Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Supply Chain Management (SCM), Customer Relationship Management (CRM)).
(10) Robots:
Refers to multi-functional single-axis or multi-axis, fully automatic or semi-automatic mechanical devices, which can perform various production activities, provide services or have the function of interacting with people through programmed actions.
(11) Additive manufacturing:
Refers to the use of additive manufacturing, based on the computer-aided design (CAD) data model, and layer-by-layer stacking of additional materials to manufacture lightweight products, reduce the number of assembly parts, save time and cost, and achieve multiple applicability .



Intelligent function
(1) Visualization of production information:
It refers to the realization of data integration and visual management of production information through mobile or display devices.
(2) Fault prediction:
It refers to predicting machine abnormalities in advance through data analysis, and performing maintenance and maintenance in advance to reduce the risk of machine failure.
(3) Accuracy compensation:
It refers to the control and compensation of dynamic errors for the required output of the equipment.
(4) Automatic parameter setting:
For registered product information, the process parameters of the product can be imported through the system to improve operational efficiency; or through the accumulation and analysis of process parameter records, optimized parameters can be automatically generated to improve process quality.
(5) Automatic control:
It refers to the calculation of production data and feedback signals collected by the digital information management system, and sends out control instructions to enable the control system to achieve automatic adjustment functions.
(6) Automatic scheduling:
Refers to different work processes, using data analysis and algorithms to automatically generate production schedules.
(7) Application service software:
Refers to intelligent application software that provides services such as design, scheduling, management, processing, or testing.
(8) Flexible production:
Refers to the production operation that can be flexibly adjusted through the control system or other software and hardware equipment in response to the needs of small amount of variety or schedule adjustment.
(9) Mixed line production:
Refers to the ability to produce products of different styles or specifications on a single production line.


